2023-12-16 12:26:00
Thyroid Health Redefined Introducing our State of the Art ELISA Product Range
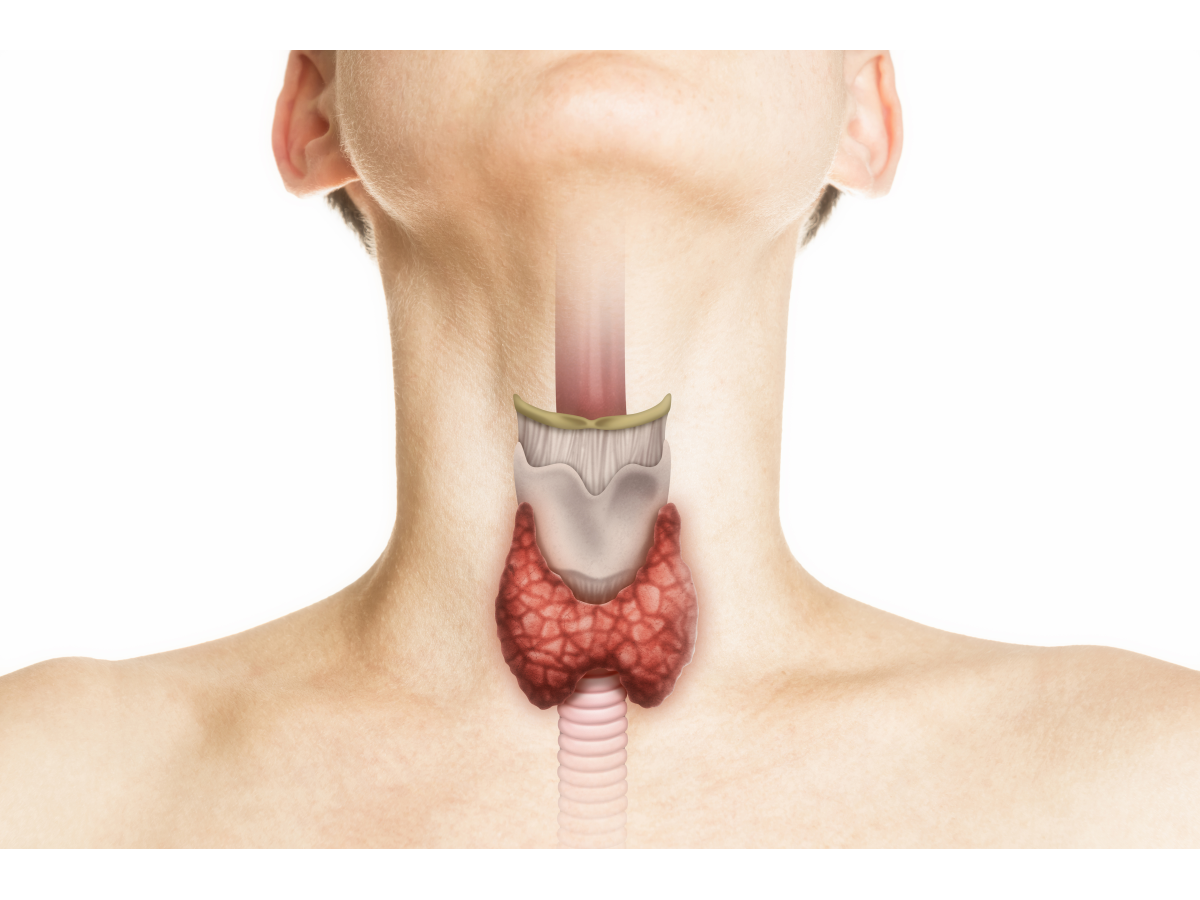
Thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck under the skin.
An Overview of Thyroid Dysfunction:
Thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck under the skin. Being a part of the Endocrine system, it controls many of our body's important functions by producing and secreting certain hormones.
The hormones secreted are.
Thyroxine (T4): Which is largely inactive and is converted to T3.
Triiodothyronine (T3): Though less T3 is produced, it plays a greater role on our metabolism.
Reverse T3: It is an isomer of T3, secreted in small quantity and reverses the effect of T3.
Calcitonin: Regulates the amount of calcium in one’s blood.
Thyroid Hormones and its Function:
It plays an important role in controlling the speed of metabolism. Thyroid hormones help to regulate many crucial bodily functions such as heart rate, body weight, muscle strength and control, breathing, body temperature, bone loss, blood lipid levels, menstrual cycles, central nervous system (CNS) and energy expenditure.
What Is Thyroid Function Test (TFT)?
Thyroid function tests are usually done to find out whether the thyroid gland is working properly. This is mainly to diagnose an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) and an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism).
People with Type 1 diabetes, Celiac disease, Addison's disease, Down's syndrome and Turner syndrome have an increased risk of thyroid problems and are often advised to have thyroid function test undertaken each year.
Thyroid Function Test:
TSH Test: The TSH test is often done first. If the thyroid hormone levels in blood are too low, your pituitary gland makes larger amounts of TSH to stimulate production of thyroid hormone and vice versa.
T4 Test: A high level of T4 indicates hyperthyroidism. Most of the T4 in body is bound to protein and a small percentage is free, together called Total T4. We need to monitor T4 levels if you're taking thyroid hormone replacement therapy (medication), to check underactive thyroid in new-borns, evaluate n/ conditions like goitre, thyroid nodules and issues with pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
Free T4 Test: A small portion of T4 is not bound to proteins and are called free T4, which are readily available for our body to use. High free T4 above normal range could mean you have an overactive thyroid also seen in Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder. Abnormally low free T4 levels may signal hypothyroidism.
T3 Test: T3 is a thyroid hormone released by thyroid gland, mostly exists as a bound form with proteins. Total T3 refers to the collection of both bound and unbound forms of T3 circulating in the blood. T3 test is most often used to diagnose hyperthyroidism.
Free T3 Test: Free T3 are unbound T3 that enters one’s body tissues where it's needed. Free T3 is in a small percentage compared to Total T3. However, measuring free T3 is more accurate than measuring Total T3 as it represents the immediately available thyroid hormone which can be used.